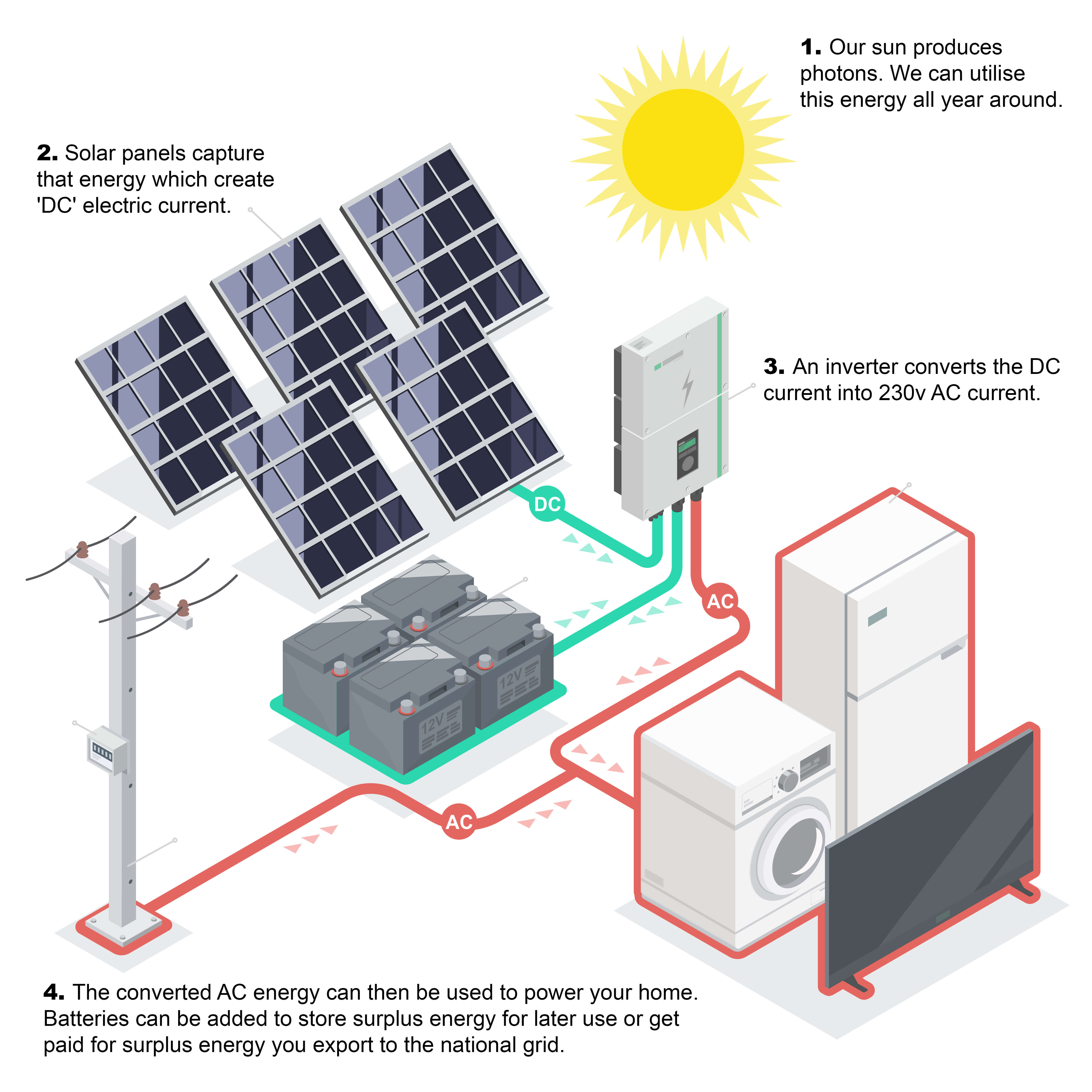
In our pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, solar photovoltaics (PV) emerges as a leading technology. A type of solar power technology, solar PV transforms sunlight into electricity. But how does this happen? Let's delve into this fascinating topic and uncover the science and benefits of solar PV.
Solar Photovoltaics (PV): The Science Behind the Power
Solar PV systems operate using the photovoltaic effect. It's a physical and chemical phenomenon first observed by French physicist Edmond Becquerel in 1839. It revolves around releasing electric current in a material after exposure to light.
Anatomy of a Solar PV Cell
The journey of sunlight to electricity within a PV system starts with the solar cell, the building block of solar PV technology. This cell contains semiconductor material, typically silicon, which possesses specific properties essential for the photovoltaic process.
When sunlight strikes the cell, its energy dislodges electrons within the silicon semiconductor. This displacement of electrons initiates an electric current, the direct current (DC). The photovoltaic effect is transforming light (photons) into electricity (voltage) at the atomic level.
The Journey from DC to AC Power
Electricity produced by solar PV cells is in direct current (DC) form. Still, the power supplied to households and businesses is typically alternating current (AC). Hence, an integral component of any solar PV system is an inverter, which converts DC electricity into AC electricity, making it usable for standard appliances and the electric grid.
Harnessing the Power: Solar PV System Configurations
Three main solar PV system configurations are designed to meet varied power requirements: standalone, grid-tied, and hybrid.
Standalone PV Systems
Standalone PV or off-grid systems operate independently from the electric grid. They rely on batteries to store solar-generated electricity during nighttime or low-light conditions. These systems often include a diesel generator for backup.
Grid-tied PV Systems
As the name suggests, grid-tied PV systems are connected to the local electric grid. Excess power generated by the system is fed back into the grid, and power can be drawn from the grid when necessary. This configuration is most common in urban settings.
Hybrid PV Systems
Hybrid systems are a combination of standalone and grid-tied systems. They're connected to the grid and have a battery for energy storage. This type offers the benefits of both systems and provides a more reliable power supply.
Why Choose Solar PV? Environmental and Economic Benefits
Harnessing solar energy through photovoltaic technology brings many benefits, including environmental protection and economic advantages.
Environmental Sustainability
Solar PV systems generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. By reducing dependence on fossil fuels, we can significantly decrease our carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts in mitigating climate change.
Economic Advantages
Solar PV systems provide cost savings over time. The sun's energy is free, so once the system is installed, the cost of electricity generation is virtually zero. Additionally, feeding excess power back to the grid in grid-tied systems can earn the user credit, further offsetting the initial installation cost.
The Future is Bright with Solar PV
Harnessing the sun's power through solar PV technology offers an environmentally friendly and economically viable path towards a sustainable energy future. As we continue to innovate and improve this technology, the potential for solar energy seems unlimited. It's more than just a trend; it's a solution that is here to stay.
How solar works.